Vegetable oil is the label used to describe the range of oils derived from plants, including olive oil, sunflower oil, canola oil, soybean oil, etc.
The name is a little misleading, as vegetable oil doesn’t always come from vegetables. It is extracted from different types of fruits, seeds, grains, and nuts. Vegetable oil comes in many varieties for many cooking purposes. The healthiest vegetable oils are canola; corn, olive; peanut; safflower; soybean, sunflower.
Even the healthiest oils should be used in moderation since they are high in calories and primarily fat. When cooking with vegetable oils, consider the different types of fat.
Saturated fats: Saturated fats usually come from animal sources like lard and butter. They lead to higher cholesterol levels in your blood, putting you at risk for heart and cardiovascular diseases. When choosing an oil, look for one that is low in saturated fat.
Trans fats: Like saturated fat, trans fat contributes to an increased risk of heart and cardiovascular diseases. These fats are from foods that are high in hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils, such as processed food. These should be avoided when possible.
Monounsaturated fats: These are also called omega-9 fatty acid and oleic acid. Monounsaturated fats contribute to good cholesterol levels and reduce your risk of heart and cardiovascular diseases. Olive oil, canola oil, sunflower oil, hazelnut oil, and almond oil are all known for being high in monounsaturated fats.
Polyunsaturated fats: These are also called omega-3 and omega-6 acids. This type of fat helps to maintain cell membranes that regulate your body’s processes, like managing cholesterol metabolism in your bloodstream. Polyunsaturated fats also help your body absorb the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, E, and K.
Olive oil
Olive oil is one of the healthiest oils there are; it is really the queen of oils. It’s made from the fruit of the olive tree. Olive oil contains mostly healthy monounsaturated fats, which may help lower your risk of heart disease. They may also help regulate blood sugar.
The most popular olive oil choice is Extra Virgin (also known as EVOO) and made from pressed olives. It’s this primary squeeze that delivers the rawest goodness of the fruit, so when you can, EVOO is the best choice. Not only is it more robust in flavor, but it also contains the most antioxidants.
If you prefer a lighter flavor, then virgin olive oil is your next best option. It’s the second press of the olive and is usually lighter in color as well as flavor.
Olive oil is by far the superior oil for cooking due to its versatility – you can cook with it, use it in salad dressings, or even just mop it up with some crusty bread.

Olive Oil Nutrition Facts
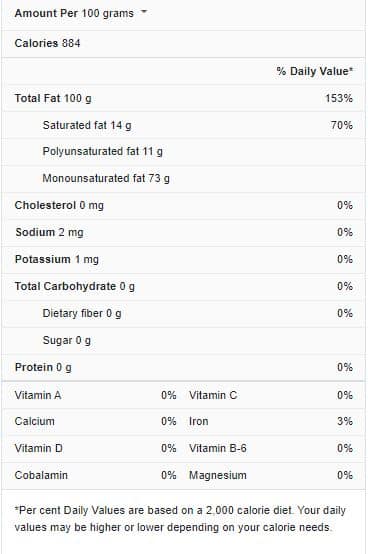
Olive oil and vegetable oil: Which is healthier?
Plant oils are a common pantry staple often used for cooking practices like sautéing or frying vegetables, making sauces, drizzling onto pizzas, and preventing pasta from sticking together.
Olive oil and vegetable oils are some of the most popular plant oils used worldwide, each displaying unique characteristics.
Let’s look at the differences between olive oil and vegetable oil, including their best uses, taste, nutrition, and potential health benefits.
Olive oil and vegetable oil differ in how they’re made, their best culinary uses, flavors, and nutritional composition.
Olive oil
- It is derived from processed olives
- Used mainly in salad dressing, sautéing, and for a bread dip
- Possesses vitamin K and E (in extra virgin varieties)
- Very high in antioxidants
- Olive oil is not processed (depends on the form, extra virgin varieties are the least processed)
- Olive oil has a boiling point of 390OF(200oC)
Vegetable oil
- It is derived from a blend of fats from multiple plant sources, like sunflower, corn, canola, soy, and safflower
- Used mainly in baking and frying
- The nutrients depend on the oil blend but usually retain minimal trace nutrients after processing (The possibilities are endless).
- Has no antioxidants
- Vegetable oil is highly processed
- And has a boiling point of 400oF(205oC)
While olive oil and vegetable oils have different culinary uses, the healthiest option is extra virgin olive oil, which is the least processed and offers the most beneficial compounds.
Can you substitute Olive oil for vegetable oil
Extra virgin olive oil is arguably the healthiest substitute for vegetable oil as it’s high in good fats and powerful antioxidants. However, it has a robust flavor, so it’s not ideal for baking. It’s best used in frying on low to medium heat and dressings.
Olive oil can be substituted for vegetable oil in dressings or marinades and sautéed over low to medium heat. Since olive oil has a low smoke point, it shouldn’t be used for recipes that require high heat. Olive oil isn’t a good choice for baked goods due to its strong flavor.
If your recipe calls for vegetable or canola oil, you should definitely substitute those oils with gourmet extra virgin olive oil. Any dessert recipe that calls for vegetable oil as an ingredient is a perfect choice for olive oil. In these recipes, the swap would be a one-to-one ratio. In other words, if the recipe calls for one cup of vegetable oil, you would simply use extra virgin olive oil. Imagine how the smooth, delicious flavor of gourmet olive oil will enhance chocolate or a carrot cake!
Substitute Olive oil for vegetable oil in brownies
A useful substitute for vegetable oil in a brownie recipe is olive oil. Use a light or extra light olive oil as they are highly refined and can affect the taste and texture of your brownies. Hence, avoid using strongly-flavored olive oil, and use the same concentration of olive oil as the amount of vegetable oil.
Substitute Olive oil for vegetable oil in frying
smoke points are of the essence if you want to try substituting olive oil for vegetable oil when sautéing. Olive oil has a lower smoke point, so you’ll need to turn the heat down to medium. You can also combine olive oil with butter, which allows cooking at a higher heat.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
What is the healthiest oil to fry with?
Oils that contain lower levels of linoleic acid, such as olive and canola oil, are better for frying. Polyunsaturated oils, such as corn, sunflower, and safflower, are best used in dressings rather than cooking.
What oil is best for high heat?
The best oils for standing up to high heat during frying are avocado, peanut, canola, sunflower, and sesame oil. These oils have a high smoke point (400°F and higher), which means they are better suited for cooking at higher temperatures.
How bad is vegetable oil for you?
Vegetable oils generally seem to be healthy sources of fat. Hydrogenated vegetable oils that are high in unhealthy trans fats are an exception to this. Some nutritionists are also concerned about the high amounts of polyunsaturated omega-6 fats found in certain vegetable oils.
Conclusion
Extra virgin olive oil is arguably the healthiest substitute for vegetable oil as it’s high in good fats and powerful antioxidants. However, it has a robust flavor, so it’s not ideal for baking. It’s best used in frying on low to medium heat and dressings.

