If you enjoy baking cakes, you have probably come across shortening recipes. Notably, shortening in cake produces a lovely texture that is soft, fluffy, and light.
However, what can you do if you run out of shortening in the middle of a baking task and realize you don’t have any at hand? No need to panic anymore; there are some excellent substitutes for shortening in a cake.
Read on as you learn more about shortening in cake and delectable recipes you can try with it. In addition, I have also highlighted befitting substitutes for shortening in a cake for days you are in a pinch.

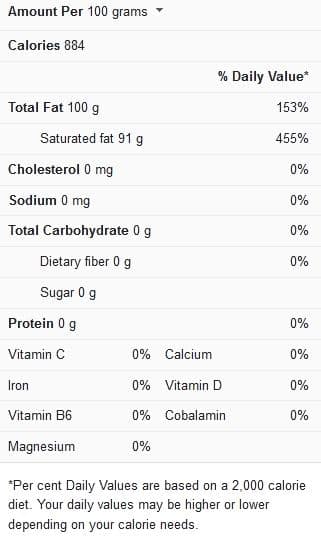
Shortening nutrition facts
What is shortening
Shortening is mostly solid fat derived from vegetable oils like soybean and sometimes cottonseed that have been artificially hydrogenated into a solid state. Since it is hydrogenated vegetable oil, it extends the shelf life of foods.
Trans fats are formulated due to this chemical process, and their ingestion raises your risk of heart disease and stroke.
Shortening is invented in the early 1900s as a substitute for animal lard, which has a similar consistency. Notably, you should know that one of the old-fashioned ingredients for manufacturing “short doughs” is vegetable shortening.
Since the mid-1990s, when the link between shortening and health hazards was rumored, vegetable shortening brands have gone above and beyond to disassociate themselves from trans fats.
Also known as vegetable shortening, this ingredient is used in various dishes, ranging from handmade flour tortillas to white cakes. While shortening does not contribute much taste to baked products like cake, it does give richness and softness – making them fluffier and flakier.
Shortening used in recipes
In baking, shortening makes products crumbly, flaky, and soft. Because it contains 100 percent fat instead of 80% fat butter and lard, shortening produces very delicate cakes, cookies, and pie crusts.
See some delectable cake recipes you can utilize shortening in:
- Vanilla Cake Recipe
- The Perfect Chocolate Cake
- Simple White Cake
- Buttercream Recipe Using Shortening
- Fabulous Red Velvet
- Yellow Cake Recipe with Milk Chocolate Frosting
- Black Chocolate Cake
- Vanilla Buttercream Frosting
- Moist White Cake
- Pound Cake
- Classic White Cake with Vanilla Buttercream Frosting
- Cream Cheese Pound Cake
- Starlight Cake
- Red Velvet Cake with Snow White Frosting
- Vegan Buttercream
Substitutes for shortening in cake
These alternatives will suffice if you don’t want to use vegetable shortening – or you do not have any at hand.
Many of these substitutions will go unnoticed, so you may make your favorite cake recipes without anyone noticing that they are missing shortening.
Butter

Butter is an excellent substitute for shortening in your cake recipe.
Though shortening can be substituted with butter, the moisture content of the butter should be considered before making the switch.
While shortening is entirely composed of fat, butter contains a little water, and as a result, shortening adds additional fat, resulting in increased richness and softness.
All of these substances have their melting points. Despite these changes, many community members have experienced success substituting butter for vegetable shortening.
So, if you don’t have any shortening on hand, use butter instead. Although your baked items like cakes won’t be as flaky, they will have a deep and buttery flavor.
Coconut oil

Another excellent shortening substitute is coconut oil.
This substitute also has a similar texture as shortening; plus, it is a vegan item. You can replace it one-for-one, but keep in mind that your baked items will likely have a slight coconut flavor.
Coconut oil, unlike shortenings, is a healthier option – it is chemical-free because it’s natural and organic.
Notably, coconut oil has a lower melting point than shortening, similar to butter. You may avoid this problem by chilling your dough sufficiently before baking it.
Coconut oil is used to grease cake pans, muffin tins, and baking dishes due to its high smoke point.
With good cause, coconut oil has become a favorite of the whole food movement. It is thought to be a good fat with antimicrobial characteristics. It’s also great in baked products like cakes.
Ghee

Ghee is simply butter that has been processed to remove the water and milk particles. Ghee is similar to shortening in that it is prepared by slowly boiling butter until all of the water has evaporated.
You can replace shortening with ghee in any cake recipe that calls for it, especially when you need a buttery taste boost.
Remarkably, vitamins, antioxidants, and healthful fats are abundant in ghee. While fat should be ingested in moderation, studies have shown that fatty foods like ghee can aid in the absorption of certain vitamins and minerals.
It may be considered a healthier alternative since ghee has a great nutritional value and low-fat content. When baking, such as greasing cake tins or mixing batter, ghee is also the preferable substitute.
Notably, ghee can be used in place of vegetable shortening in a one-to-one ratio.
Frequently asked questions (FAQs)
Is vegetable oil the same as liquid shortening?
The solid characteristic is the essential difference between vegetable oil and shortening. At normal temperature, shortening solidifies, whereas oil does not. In most cases, vegetable oil and melted vegetable shortening can be used interchangeably in recipes.
Is shortening a better alternative to butter?
It was also healthier until recently because it had less saturated fat than butter and lard. However, we know now that highly processed shortening has no health benefits and may even be less nutritious than butter.
Why is it tagged “shortening”?
Shortening gets its name because it causes the gluten strands in the dough to shorten. Wheat gluten generates elastic fibers and produces a dough that stretches, making it ideal for dishes that need to be stretched and molded, such as pizza dough.
Conclusion
If you are concerned that shortening is harmful to your health, we have some excellent news for you. Shortening was originally produced with trans-fatty acids, although today, many brands now do not include them.
At room temperature, shortening is solid saturated fat – this means you will need to find another solid fat at room temperature, preferably with the same low moisture content as shortening.
These are a few shortening substitutions that will still produce the delectable cake you desire – considering both texture and flavor.
