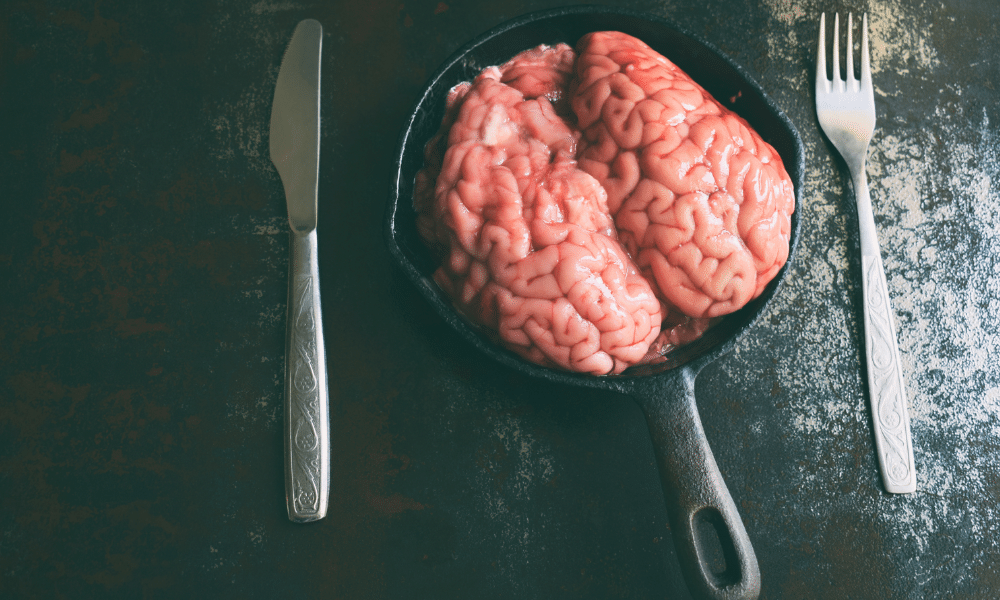
Those who have not had a chance to try brain are probably wondering what it tastes like. The first thing that will put many off is the unappetizing appearance of the brain. However, you will definitely enjoy the savory taste once you get past this. It is similar to the texture of curdled tofu, so don’t let its look keep you from trying it!
What is a Brain?
Many cultures consider the brain a delicacy, a staple food in American, French, and Asian cuisine.
Every day for breakfast, many Americans eat brains. Because they are a rich source of minerals and proteins, brains are referred to be “superfoods.” Daily brain consumption can strengthen your nervous system and shield your brain from harm.
The most well-liked meals include the brains of goats, cows, and hogs. The brains of various animals are a delicacy in all civilizations, and people discover that eating brains gives them an animalistic taste comparable to curdled tofu.
The brain is not popular gourmet food, and it is often used for medicinal purposes, so it is not recommended for people allergic to it. While it may be difficult to eat, some cultures consider it a delicacy, which makes it a delicacy for many. In fact, a few cultures eat their animal companions’ brains, and its creamy texture makes it taste similar to fish roe.
What does Brain taste like?
The brain tastes like nothing. It isn’t a very appealing flavor, but it doesn’t have to be unpleasant. A savory taste is what makes it gourmet food. There are several reasons why people like to eat the brain.
As you might guess, brains are not very tasty. But they’re very firm and have a creamy texture. They taste like fish roe but differ from other parts of the animal. Nonetheless, the brains are very popular gourmet food. They have a delicious and creamy flavor. You can eat them in any quantity. If you are curious, you can purchase them in various markets.
Brains often have a savory flavor with a bitter undertone. However, the flavor will vary based on the species. The flavor of the brain is unlike any other portion of the animal. The taste of iron in the liver or the umami-rich, gamey sensation found in kidneys doesn’t exist in the brain. The thymus or pancreatic is the closest internal organ it may be compared to in a pinch.
Do various animal species’ brains have varying flavors?
Although there is typically a slight touch of the animal’s taste in the brain, all brains tend to have a similar flavor and texture.
- One of the most popular alternatives for food, lamb’s brain has a gelatinous consistency. Some claim it has a flavor similar to sashimi and a texture that gives little resistance when eaten.
- Another popular choice with a texture similar to lamb’s brain is pig’s brain. You’ll taste a creamy, umami flavor with a light undertone of pork, but it isn’t an overpowering dish. Chinese cuisine frequently uses pig brains, which are prepared in various ways.
- Chicken brains are considerably smaller than most other foods you’ll get the chance to consume. Each one is about the size of a bird’s eyeball, so you’ll need a lot to make a substantial dinner. They are fatty organs with a distinct sponge-like feel and a flavor similar to chicken fat.
- The texture of a goat’s brain is comparable to a lamb’s brain. Although its flavor is frequently bland, this can be the best choice for you if you want meals without a strong flavor.
- Cow brains have a very subtle beef flavor and are also rather bland. However, in certain regions of the world, the ingestion of this offal is prohibited. Although unlikely, it is possible to get mad cow disease, also known as a bovine spongiform encephalopathy.
Which nations like eating them?
In the Sichuan area, the Chinese enjoy adding brains, whether grilled or in a delicious hotpot. In Southern China, Tianma Zhunao Tang is more often consumed, and the pig’s brain is a key component of this cuisine.
In Cuba, brain fritters are a highly regarded meal. Before frying the organs till golden brown, they cover them with bread crumbs.
In Indonesia, the cow’s brain is a favored food component. one of the Minangkabau people’s signature dishes. They include them in a curry (gulai banak) with a mouthwatering sauce prepared from coconut milk.
In tête de veau, which entails cooking a whole calf’s head for many hours until soft, brains are used in French cuisine. Other European nations, including Italy, Germany, and Belgium, are also big fans of this meal.
Maghaz is a popular dish in Muslim cuisine. It includes presenting a goat, sheep, or cow’s brain with gravy and is a traditional dish from the Indian subcontinent. The brain and other lamb organs are used in Turkey’s dish called beyin sogus.
Does Brain have a gamey flavor?
The taste of the brain varies between different types of animals. Although it is not gamey like the heart or liver, the flavor is savory and sweet. Unlike other body parts, the brain is not gamey and has a creamy texture similar to scrambled eggs or tofu. You can also eat the brain raw, but be careful not to try it if you’re unsure of its taste.
While the brain is different from the kidney, it is similar to sweetbreads. Its flavor is not gamey or meaty like kidney, but it has a savory, buttery undertone. The flavor of the brain isn’t so gamey and doesn’t resemble that of any other part of the body. The meaty part is often fried or baked in Turkish cuisine or consumed raw as a salad. In some cultures, it is considered a delicacy and is served as a garnish.
What are the benefits of eating Brain?
Not only does it taste good, but it is also nutritious. Food has several essential human nutrients, contains no cholesterol and is a good source of proteins and antioxidants.
1: A happier mood
Most animal brains include B vitamins, which are well-known for their energizing and mood-lifting properties.
By maintaining the brain free of metabolic byproducts like homocysteine that may otherwise pave the foundation for depression, B vitamins have been demonstrated to protect against neurodegenerative consequences. Don’t overlook the link between cholesterol and enhanced mood and cognitive function.
2: Improved hormonal equilibrium
“Youth-associated hormones” are extracted from the brain as food. Pregnenolone, progesterone, and DHEA are three of the most abundant hormones in animal brains.
Pregnenolone
Pregnenolone has been listed first since it is the precursor for producing the other two “youth-associated” hormones.
Pregnenolone obtained from the diet is eventually transformed into progesterone, DHEA, testosterone, and/or estrogen. But it also offers a unique set of advantages.
Due to DHEA’s capacity to encourage healthy muscular contraction, particularly around the face, many people experience a “face-lifting” effect.
Progesterone
Although progesterone is often associated with pregnancy (thus the name), it is much more.
Many of the most vital glands in your immune system are shielded from damage caused by cortisol by progesterone, and it is also well known for being beneficial to the skin.
DHEA is another vital hormone that supports youth. Its anti-catabolic properties, like progesterone, prevent cortisol and other stress hormones from having negative consequences. Increased bone and muscular development are related to higher DHEA levels.
3: Improved cognitive ability
The brain as food can improve cognitive function and increase processing speed because of the unique combination of vitamins, minerals, hormones, and growth factors it contains.
Animal brain in food may help:
- Thinking flexibly (neuroplasticity)
- development of fresh neurons (neurogenesis)
- positive pattern development (long-term potentiation)
Fears of consuming Brain
Some individuals are wary about eating animal brains due to the widespread media attention given to prison-related illnesses, most notably mad cow disease.
Thank goodness, mad cow disease is now extinct. Additionally, young animals that produce brains for food do not have mad cow disease.
Poor-quality goods are a more pertinent worry than prion infections. Poorly handled animals may have brains that are more fibrotic and less nourished.
According to certain studies, the polyamine proteins in animal products may cause the diner to experience feelings or memories. Make every effort to obtain brains from healthy, content animals like those from a nearby organic or ethical farm. Likewise, wherever feasible, seek cattle products that have been raised on grass.
How can I find a good Brain to eat?
Talking to meat producers at your neighborhood farmers’ market is the greatest method to find the brain.
Your neighborhood butcher is the second-best place to look.
The quality animal brain can be obtained through a dried supplement if you want the advantages of the brain but don’t want to deal with finding and preparing it.
One of the few organ supplements on the market with the brain is Dr. Kiltz’s Organ Meat Supplement (most just contain liver, kidney, and heart). Any dietary supplement you select needs to meet all of the criteria below:
- independent examination for microorganisms
- independent veterinary inspection
- Utilizing freeze-drying to preserve nutrients
- Buying from young calf sources
- Certification as organic
Conclusion
The taste of brains is not particularly gamey and has a savory flavor. When cooked properly, it has a soft texture and is firm. In addition, it has a rich, creamy texture, unlike other parts of the animal. Compared to other parts of the body, brains are quite different from k and thee more firm and have a buttery undertone, making them an excellent choice for cooking.
The taste of brains is similar to that of fish. It is creamy and has a nutty flavor. It is similar to the texture of a fish’s eyeballs. But the taste of animal brains is very different from other parts of the body. Instead of meat, the brain tastes more like a fatty substance, like a nutty substance. A chicken’s brains are rich in proteins and fats.